Why Is Bitcoin So Valuable If It’s Not Backed by Anything

Bitcoin isn’t issued by a government or backed by any asset, yet it trades for tens of thousands of dollars. This article explains why Bitcoin is so valuable, what drives demand, and how crypto earns its place in global markets.
On this page
Bitcoin isn’t backed by gold, oil, or a government promise. It has no physical form and doesn’t generate cash flow. Yet, it consistently ranks among the most valuable assets in the world. For many, that sounds like a bubble. For others, it is the result of design, code, and demand working together in a way traditional assets cannot match.
This article breaks down why is bitcoin so valuable, even without backing from banks or states. It looks at the principles behind its value, such as scarcity, decentralization, and trust in the network. It also explains how cryptocurrency holds real weight in global markets despite being entirely digital.
What Gives Bitcoin Its Value?
Bitcoin doesn’t exist in any physical form. It’s not something you can hold like a coin or a bar of gold, and it’s not issued by any central bank. Still, it has value, and not a small one. That value is rooted in a specific set of economic and technical principles built into the network.
One of the most important is its limited supply. The Bitcoin protocol enforces a hard cap of 21 million coins. This fixed ceiling, combined with halving events that slow the creation of new coins over time, gives Bitcoin a deflationary character. Unlike fiat currencies, which can be printed without limit, Bitcoin’s supply is finite. That makes it more resistant to inflation.
Equally crucial is the absence of central control. There’s no single authority issuing or managing Bitcoin. It runs on a global network of independent nodes, with rules enforced by consensus. No one can alter the monetary policy or freeze accounts. This gives Bitcoin resilience and neutrality, especially in countries with unstable banking systems or currency controls.
Bitcoin also offers a secure foundation. It uses Proof-of-Work to validate and record every transaction on the blockchain. This system makes it extremely difficult to manipulate or counterfeit the network. Trust isn’t based on institutions; it’s built into the code and confirmed by the community that maintains it.
Beyond that, Bitcoin serves a real function. People use it to store and transfer value, particularly in regions where traditional financial tools are unreliable or unavailable. It’s borderless, open, and doesn’t require permission from a bank to operate.
So when people ask ‘Is bitcoin a physical coin?’, they’re usually thinking in outdated terms. Bitcoin’s value doesn’t come from what it is. It comes from what it enables.
What Does It Mean That Bitcoin Is ‘Backed by Nothing’?
One of the most common criticisms of Bitcoin is that it’s not backed by anything. It doesn’t represent ownership in a company. It isn’t tied to a physical commodity. There’s no government standing behind it. So why is Bitcoin worth anything?
To answer that, it helps to look at what gives value to any form of money. Modern fiat currencies like the US dollar are also not backed by gold or other tangible assets. Their value comes from trust in the institutions that issue them and the belief that others will accept them in exchange for goods and services.
Bitcoin works differently, but the principle is similar. What makes cryptocurrency valuable is the trust placed in its rules, its network, and its predictable supply. Bitcoin’s code enforces a strict monetary policy. Its blockchain ensures transparency. And its decentralized structure means that no single entity can change the system or inflate the supply.
It’s not backed by a vault of gold. Instead, it’s backed by a global network of users who validate transactions and uphold the protocol. Every rule is enforced by consensus. Every transaction is recorded permanently on a public ledger. This structure removes the need for intermediaries and central banks.
What gives Bitcoin its value is not what it represents on paper but how it functions in practice. People use it, hold it, and trust it to do what it promises. Over time, that trust becomes its own form of backing.
What Supports the Value of Bitcoin?
Bitcoin’s value doesn’t float on hype alone. Behind the headlines and price charts is a foundation built on real infrastructure, usage, and technical integrity. These elements don’t just explain its market presence; they help answer the deeper question: why is Bitcoin so valuable?
At the core is the blockchain itself. Every transaction on the Bitcoin network is permanently recorded on a public, tamper-resistant ledger. Each block is linked to the previous one, forming a chain that is nearly impossible to alter without rewriting the entire history. This design makes fraud incredibly difficult and gives users confidence that their balances and transfers are secure.
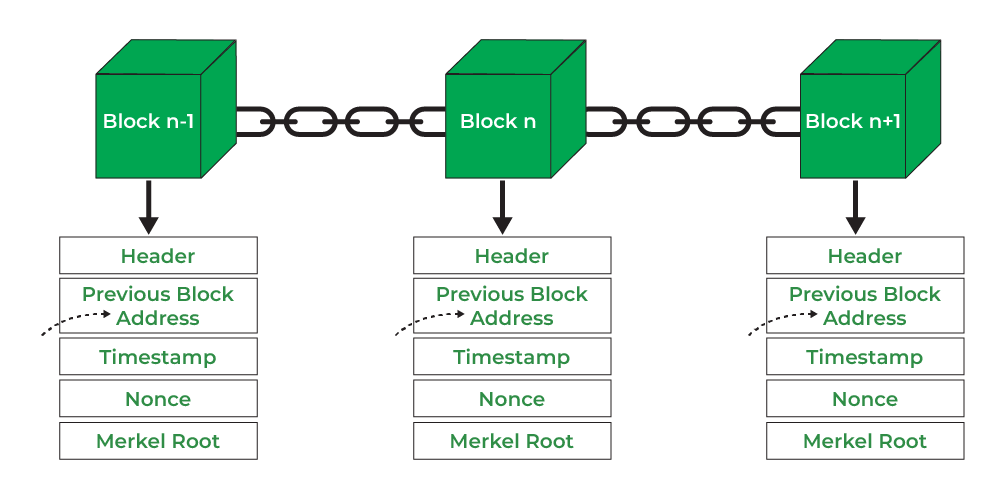
The network is another critical piece. Bitcoin is supported by tens of thousands of independent nodes around the world. These machines enforce the rules of the protocol, validate new blocks, and keep the system decentralized. The size and openness of this infrastructure make Bitcoin resilient against attacks and censorship.
The mining process, based on Proof-of-Work, requires significant computing power. This makes it expensive to manipulate the network and ensures all transactions are verified through a transparent and competitive process.
Then there is demand. Millions of users, developers, and institutions have adopted Bitcoin in some capacity. From long-term holders to payment processors and ETF managers, Bitcoin’s reach has expanded far beyond its early niche. That growing user base adds liquidity, visibility, and ultimately, trust.
In short, Bitcoin’s value is reinforced by:
- transparent and tamper-resistant blockchain
- decentralized global network with no central control
- growing ecosystem of real-world users and institutional support
Some still ask ‘is Bitcoin fiat money?’. The answer is no. Fiat currencies are issued by governments and backed by central banks. Bitcoin is not. But unlike fiat, it is not dependent on policy decisions or inflation targets. Its rules are fixed. Its supply is transparent. And its value is supported by a global network that has proven reliable for over a decade.
Key Reasons Behind Bitcoin’s Value
Bitcoin’s value doesn’t come from a single feature. It is shaped by a combination of economic principles, network design, and real-world use. These factors help explain why is cryptocurrency valuable, especially to long-term holders and institutions.
- Limited supply. Bitcoin has a fixed cap of 21 million coins. This built-in scarcity protects it from inflation and supports its role as a store of value.
- Censorship resistance. No authority can block or reverse transactions. The network operates independently of governments or centralized control.
- Global access. Anyone with an internet connection can use Bitcoin. It does not require a bank account or approval to participate.
In addition, users maintain full ownership of their funds through private keys. Bitcoin also offers complete transparency. Every transaction is publicly recorded on the blockchain and can be verified by anyone. These qualities continue to drive adoption and reinforce its value.
How Market Forces Shape the Price of Bitcoin and Other Coins
Bitcoin’s design gives it structure, but price is still driven by the market. Unlike traditional assets backed by earnings or collateral, cryptocurrencies are valued through supply and demand. To understand why does crypto have value, it’s necessary to look at how external forces affect pricing.
Market sentiment plays a major role. News cycles, investor expectations, and social media trends often move prices faster than technical developments. A single announcement, whether from a central bank or a tech CEO, can trigger a sudden rally or sell-off.
Supply also matters. Bitcoin’s fixed supply is well known, but available liquidity at a given time can vary. Long-term holders who move coins off exchanges tighten the market, making prices more sensitive to demand spikes. The reverse is also true during corrections.
Regulation adds another layer. Positive signals, like ETF approvals or tax clarity, tend to support prices. Uncertainty or outright bans, on the other hand, can trigger panic. Because crypto is still relatively young compared to traditional finance, regulatory events have an outsized influence.
Macroeconomic factors are also in play. Inflation, interest rates, and currency instability can shift investor behavior. In periods of economic stress, some turn to crypto as a hedge, while others retreat to safer assets. These moves impact both price and volume.
In the end, crypto’s value isn’t set by formula. It moves with perception, confidence, and momentum. And that makes understanding the broader market essential to understanding the asset itself.
The information published on CoinRevolution is intended solely for general knowledge and should not be considered financial advice.
While we aim to keep our content accurate and current, we make no warranties regarding its completeness, reliability, or precision. CoinRevolution bears no responsibility for any losses, errors, or decisions made based on the material provided. Always do your own research before making financial choices, and consult with a qualified professional. For more details, refer to our Terms of Use, Privacy Policy, and Disclaimers.