8 DeFi Examples That Are Killing Traditional Banks

From yield farming to cross-border payments, explore how DeFi use cases unlock new ways to lend, trade, and tokenize assets without intermediaries.
On this page
Decentralized finance (DeFi) is no longer a niche experiment. It is reshaping how financial services are built, accessed, and scaled. By replacing intermediaries with smart contracts and open protocols, DeFi lets anyone lend, borrow, trade, and insure assets with greater transparency and control. This article examines the most practical DeFi use cases and how they are transforming key areas of the global economy.
What Is DeFi and How Does It Work?
Decentralized finance, or DeFi, is a category of blockchain-based financial services that operate without centralized intermediaries such as banks or brokerages. Instead, decentralized finance platforms use smart contracts, self-executing code on public blockchains, to automate transactions and enforce rules transparently.
DeFi reimagines traditional finance by replacing closed, permissioned systems with open, programmable networks. Anyone with internet access and a crypto wallet can use financial tools like lending, borrowing, trading, and saving without relying on a third party.
One of the most prominent DeFi examples is peer-to-peer lending. Unlike conventional banking, where credit decisions are centralized and opaque, DeFi protocols such as Aave and Compound let users lend and borrow directly through collateralized smart contracts. This increases transparency, lowers entry barriers, and removes the inefficiencies of intermediaries.
Another key feature of DeFi is composability. Protocols can integrate and interact freely, forming flexible and interconnected systems. A user might earn interest on a stablecoin in one platform while using that same token as collateral in another.
By removing intermediaries and giving users full control of their assets, DeFi shifts power to individuals. Though still evolving, it offers the foundation for a financial system that is open, transparent, and accessible worldwide.
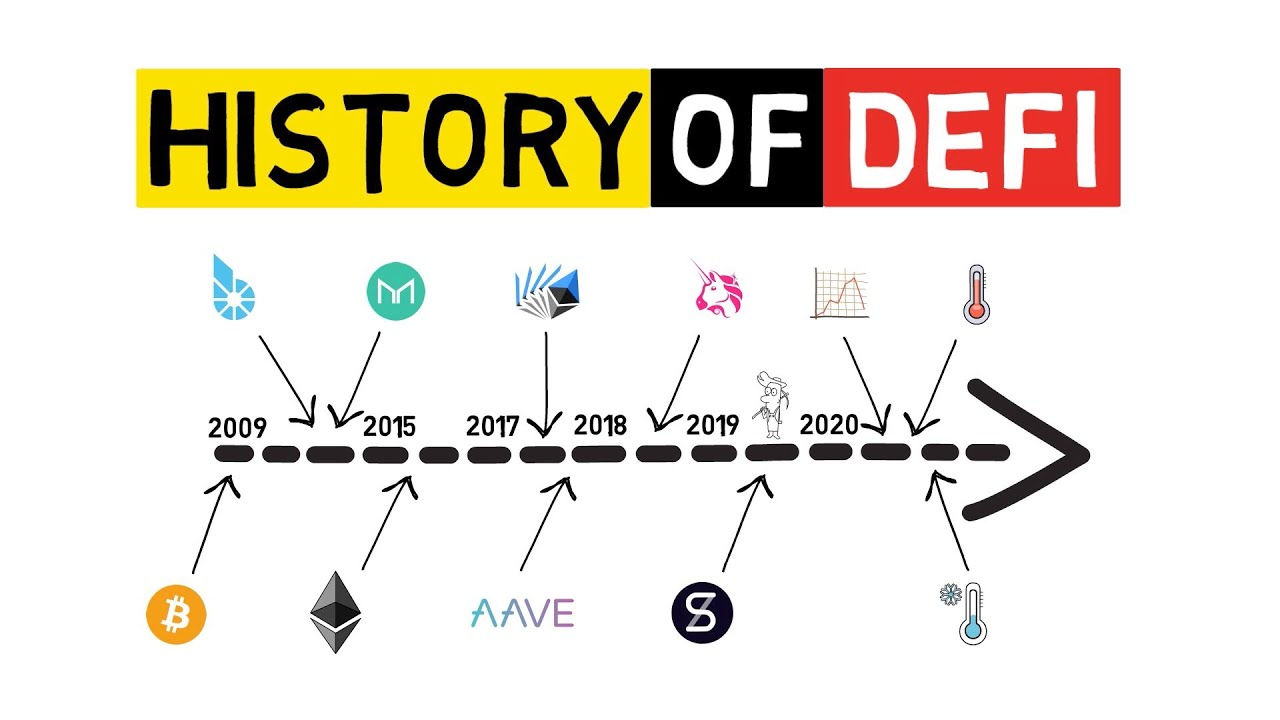
The Development Journey of Decentralized Finance
Decentralized finance began with basic token swaps and has grown into a complex ecosystem that rivals, and often outperforms, traditional financial infrastructure. What started with platforms like MakerDAO and Uniswap has become a network of thousands of protocols offering lending, derivatives, insurance, asset management, and more.
Early DeFi focused on building core tools. MakerDAO introduced decentralized stablecoins; Uniswap brought automated market makers into the mainstream. These innovations laid the foundation for trustless transactions and user-controlled liquidity.
The next phase introduced composability and yield optimization. Platforms like Yearn Finance began aggregating services across protocols, making it easier to move capital efficiently. Cross-chain interoperability has since unlocked new forms of liquidity and expanded access to global markets.
A key benefits of DeFi is its permissionless structure. Anyone can take part in financial activity without geographic or bureaucratic restrictions. DeFi removes gatekeepers and gives users full control of their assets and data.
Today, DeFi is shifting toward real-world use and regulatory alignment. Tokenized real estate, decentralized identity, and compliant stablecoins are creating new DeFi opportunities in mainstream finance, business, and public infrastructure.
Once an experiment in autonomy, DeFi is now a credible alternative to legacy systems. Its future depends on secure scaling, better user experience, and tighter integration with traditional finance.
DeFi Use Cases
Decentralized finance has introduced a broad set of real-world applications that extend well beyond crypto trading. From lending and borrowing to insurance, payments, and asset tokenization, DeFi is changing how individuals and businesses manage money.
Here are some of the most significant DeFi use cases, each solving long-standing inefficiencies in traditional finance. These examples of DeFi show how smart contracts and open protocols can simplify financial services, expand access, and remove the need for centralized intermediaries.
What Is Yield Farming in DeFi?
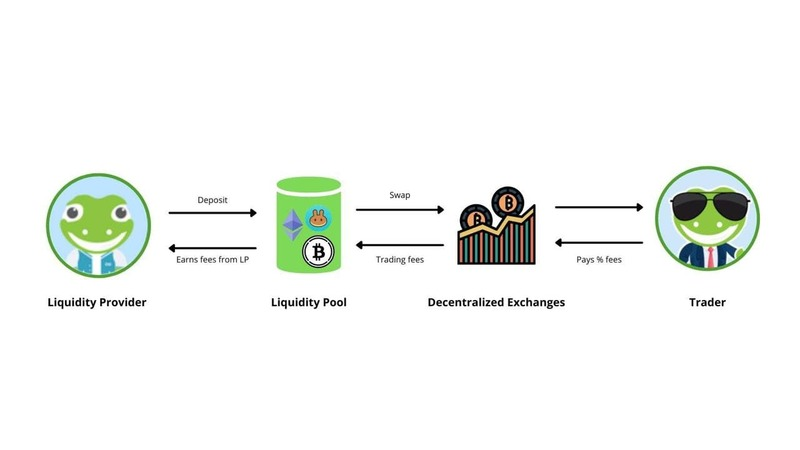
Yield farming is a strategy in decentralized finance that allows users to earn passive income by providing liquidity to DeFi protocols. Also known as liquidity mining, this process involves depositing crypto assets into smart contracts called liquidity pools. In return, users receive rewards in the form of transaction fees, governance tokens, or interest.
At its core, yield farming incentivizes users to lock up their tokens so others can trade or borrow against them. These locked assets provide the liquidity necessary for decentralized exchanges (DEXs) and lending platforms to function smoothly. In exchange for this service, users are compensated based on how much liquidity they contribute and how long they keep their assets in the pool.
Many yield farming platforms issue Liquidity Provider (LP) tokens to represent a user’s share of the pool. These LP tokens can often be staked in additional protocols for even more rewards, creating a stackable yield effect. Some of the most well-known platforms that offer yield farming include Yearn Finance, Curve, Aave, and Balancer.
Typical steps involved in yield farming:
- Choose a DeFi platform and a liquidity pool to join.
- Deposit a pair of assets (e.g., ETH and USDC) into the pool.
- Receive LP tokens that represent your share.
- Stake LP tokens in other protocols (optional).
- Earn rewards over time, which can be claimed or reinvested.
While yield farming can be highly profitable, it comes with risks such as impermanent loss, smart contract vulnerabilities, and volatile returns. Proper research and risk management are essential before participating.
DEX Platforms: A Core Pillar of DeFi
Decentralized exchanges, or DEXs, are blockchain platforms that let users trade cryptocurrencies directly without a central authority. Instead of intermediaries managing orders and holding assets, DEXs use smart contracts to automate and secure transactions. This peer-to-peer model ensures users retain full control of their funds.
DEXs are a cornerstone of the DeFi ecosystem. They support open, permissionless trading, allowing anyone with a crypto wallet to participate without registration or identity checks. This broad accessibility reflects the core principles of decentralization and financial autonomy.
Most DEXs use automated market makers (AMMs), which rely on liquidity pools rather than order books to process trades. Users add tokens to these pools and earn a share of the trading fees in return. Leading AMM-based DEXs include Uniswap, Curve, and Balancer. Some platforms, like dYdX and XRPL’s native exchange, combine AMMs with order books to support more advanced trading features.
By removing intermediaries and limiting censorship, DEXs improve transparency, strengthen security, and lower costs. As DeFi evolves, DEXs continue to play a central role in shaping its infrastructure.
Payments and Transactions with Stablecoins
Stablecoins play a crucial role in DeFi by enabling fast, secure, and low-volatility transactions. Pegged to stable assets like the US dollar, euro, or gold, they provide a reliable medium of exchange in an otherwise volatile crypto market. This stability makes them ideal for day-to-day payments, cross-border transfers, and financial operations where price predictability matters.
In DeFi ecosystems, stablecoins are used in a variety of ways. They serve as base currencies in decentralized exchanges, collateral in lending protocols, and a unit of account for yield-generating strategies. Platforms such as MakerDAO (with DAI), Circle (with USDC), and Tether (with USDT) have established themselves as key issuers, offering widely accepted tokens backed by transparent reserve models or algorithmic mechanisms.
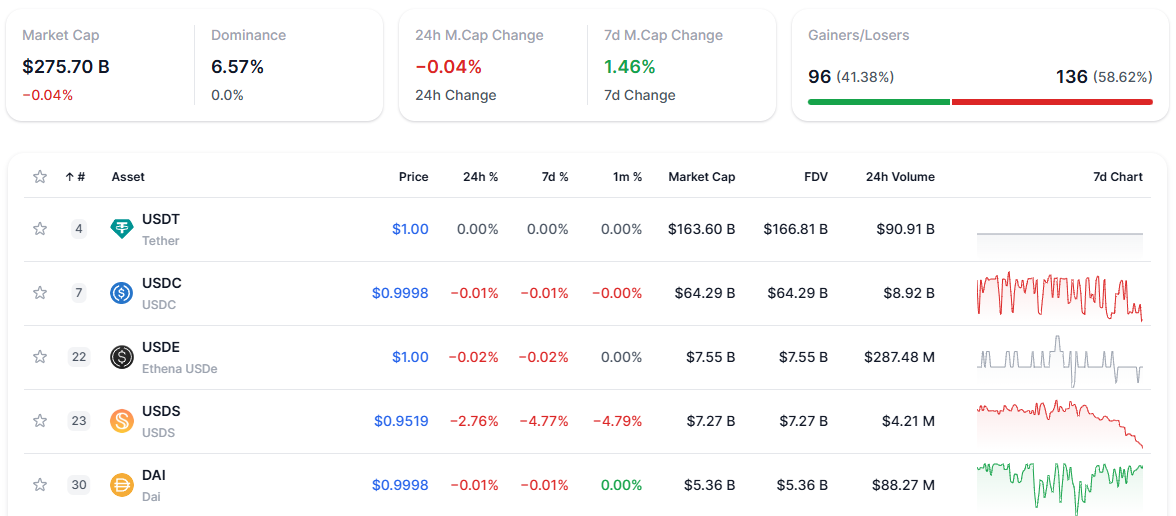
Stablecoins also simplify remittances. Traditional cross-border transfers are often slow, costly, and dependent on intermediaries. In contrast, sending stablecoins requires only a crypto wallet and internet access, with transactions settling in minutes and at a fraction of the cost. This has made stablecoins particularly attractive in regions with limited access to banking services or high currency volatility.
By combining the advantages of digital assets with price stability, stablecoins provide a practical gateway between traditional finance and the decentralized economy. They enable DeFi applications to function more predictably and appeal to a broader range of users.
Tokenization of Real-World Assets (RWAs)
Tokenization is the process of converting ownership rights to physical assets into digital tokens recorded on a blockchain. In DeFi, this makes it possible to represent and trade real-world assets (RWAs) such as real estate, commodities, bonds, and investment funds within a decentralized framework.
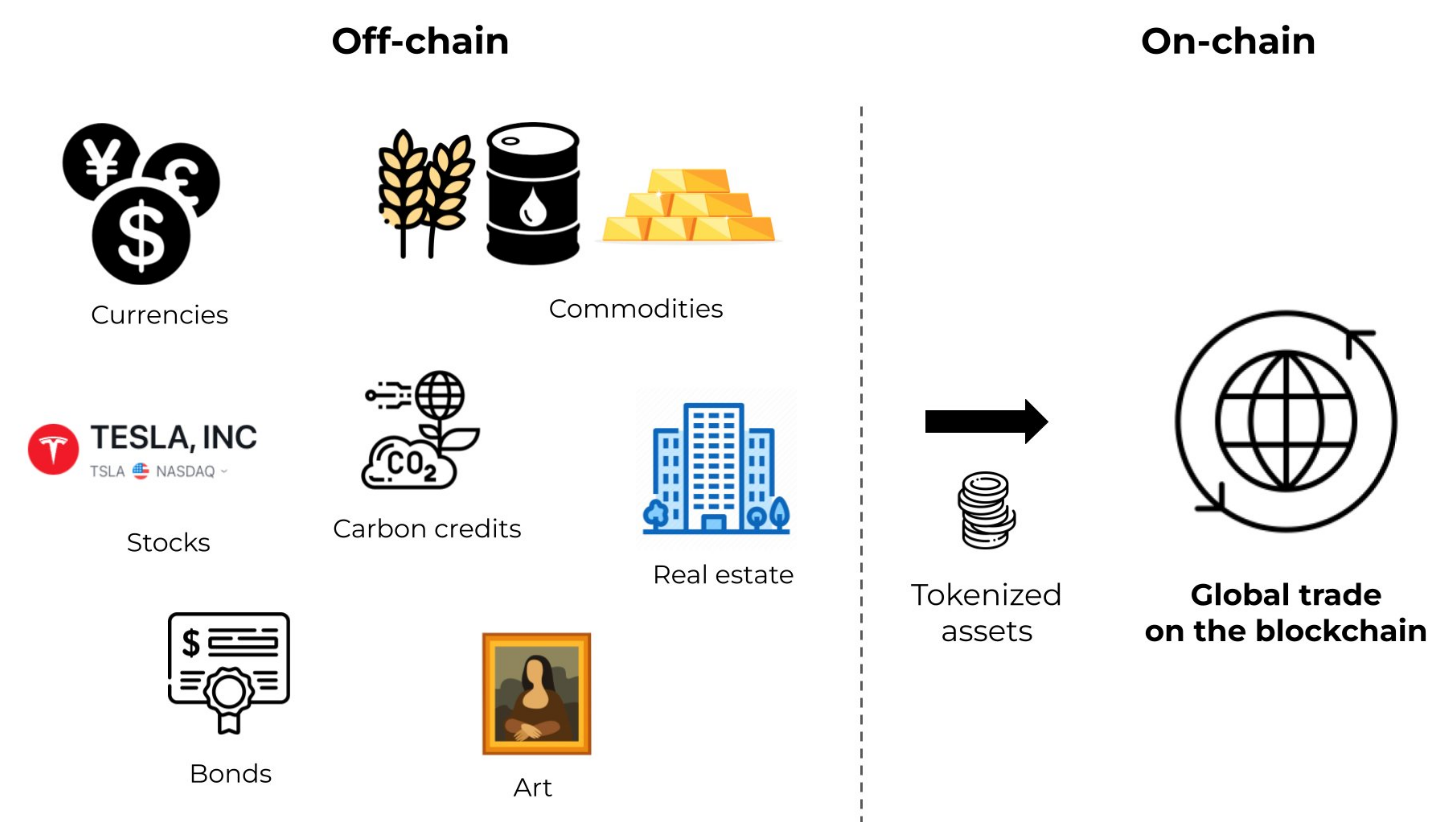
By digitizing these assets, tokenization brings clear advantages. It boosts liquidity, enables fractional ownership, and lowers the barrier to entry for investors. Instead of purchasing an entire apartment or a full stake in a private fund, users can buy a fraction—sometimes for just a few dollars. This opens access to asset classes that were once limited to institutional or high-net-worth investors.
Platforms like Centrifuge, RealT, and Securitize have led the way, connecting on-chain tokens to off-chain legal agreements. Their infrastructure ensures that each token corresponds to a legitimate claim on a real asset.
Key benefits of RWA tokenization in DeFi:
- Liquidity for assets that are typically illiquid
- Broader market access for both issuers and investors
- Transparent, tamper-proof ownership records
- Fractional ownership with low entry costs
- Faster and more efficient settlement than in traditional finance
As regulation and infrastructure continue to evolve, RWAs are poised to become a foundational component of the DeFi ecosystem.
Using DeFi for Global Money Transfers
Traditional remittance systems are expensive and slow. Western Union charges an average of 6-8% in fees for international transfers, while banks often add 3-5% in hidden exchange rate markups. A $500 transfer from the US to the Philippines typically costs $30-40 in fees and takes 3-5 business days to clear.
DeFi eliminates these inefficiencies through stablecoin transfers. Using platforms like Wise (formerly TransferWise) integrated with DeFi protocols, or direct blockchain transfers via USDC on Polygon, users can send money globally for under $1 in fees. A $500 USDC transfer settles in 2-15 minutes regardless of destination.
Several platforms are leading DeFi remittances:
- Stellar partnerships with MoneyGram enable instant USDC transfers
- Polygon-based solutions like Biconomy offer sub-$0.50 transaction fees
- Lightning Network allows Bitcoin transfers for pennies
- Celo focuses specifically on mobile-first remittances in emerging markets
| Method | Fee | Time | Requirements |
| Western Union | 6-8% | 3-5 days | Physical location, ID |
| Bank Wire | 3-5% + $25 | 1-3 days | Bank account, complex forms |
| DeFi Stablecoin | <0.1% | 2-15 minutes | Wallet, internet |
In Nigeria, where inflation exceeds 20%, workers abroad use USDC to send stable value home, bypassing naira devaluation. Filipino overseas workers save $200+ annually per family by using Polygon-based remittances instead of traditional services. Venezuelan recipients prefer DAI or USDC over bolívars due to hyperinflation.
Challenges remain: recipients need crypto literacy, local fiat on-ramps vary by region, and regulatory uncertainty persists. However, partnerships between DeFi protocols and traditional money service businesses are expanding access. As mobile wallet adoption grows, DeFi remittances could capture 20%+ of the $800 billion global remittance market by 2030.
The information published on CoinRevolution is intended solely for general knowledge and should not be considered financial advice.
While we aim to keep our content accurate and current, we make no warranties regarding its completeness, reliability, or precision. CoinRevolution bears no responsibility for any losses, errors, or decisions made based on the material provided. Always do your own research before making financial choices, and consult with a qualified professional. For more details, refer to our Terms of Use, Privacy Policy, and Disclaimers.